[ad_1]
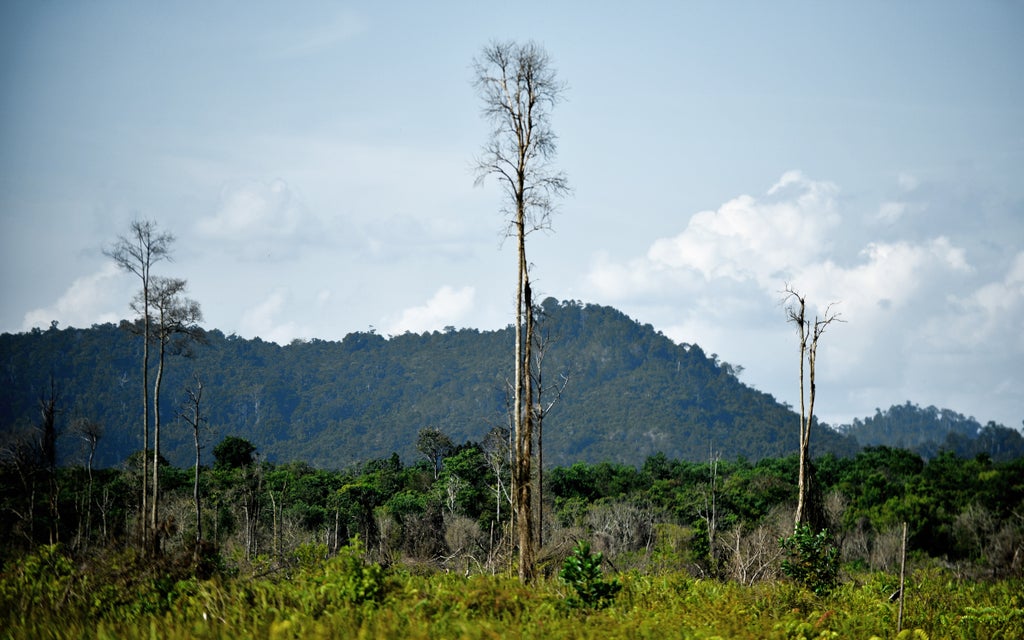

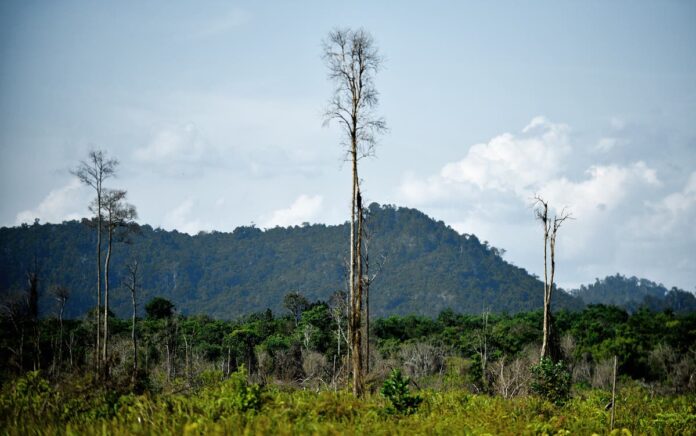
Tropical forests can regrow surprisingly quickly on abandoned lands, according to a new study that provides fresh insights for climate change mitigation.
Scientists have found that tropical forests have the potential to regrow by about 78 per cent if left untouched by humans for about 20 years, showed research published in the journal Science on Thursday.
Although tropical forests worldwide have disappeared rapidly due to deforestation, the international team of scientists, including those from Wageningen University in The Netherlands, say these secondary forests can play an important role in climate change mitigation and biodiversity and ecosystem restoration.
Currently, tropical forests continue to be cleared globally to make way for other land uses, including agriculture and livestock grazing. But the gradual abandonment of some of these lands has led to a rapid increase in forest regrowth.
To understand how the forest regrowth happens in these lands, researchers analysed patterns of forest recovery in 77 secondary forest sites in the Americas and West Africa.
They evaluated 12 features of forests related to soil, plant functioning, ecosystem structure and biodiversity.
The study found that while different attributes recover at different rates, tropical forests can recover quickly — attaining 78 per cent of their old-growth values for these attributes in 20 years, while plant community and species diversity recover in fewer than 60 years.
But the researchers added that the recovery for biomass and species composition could take about 120 years to reach 90 per cent of old-growth values, although the near-total recovery of just the soil could happen in less than 10 years.
However, the study also cautioned that there was “substantial variation” in forest regrowth across the study region.
In some abandoned areas, the scientists said there may be “arrested succession” due to the lack of seed sources or dominance of invasive grass, ferns, or woody species.
Under such conditions, management practices such as weeding, controlling invasive species, enrichment planting, and the establishment of ecological corridors are needed to safeguard multidimensional recovery, they said.
The researchers urged countries to nurture the growth of secondary forests as a low-cost, nature-based solution to meet the United Nations’ Sustainable Development goals and the United Nations’ Decade on Ecosystem Restoration goals.
“Secondary forests should be embraced as a low-cost, natural solution for ecosystem restoration, climate change mitigation, and biodiversity conservation,” they wrote in the study.
[ad_2]
Source link