[ad_1]
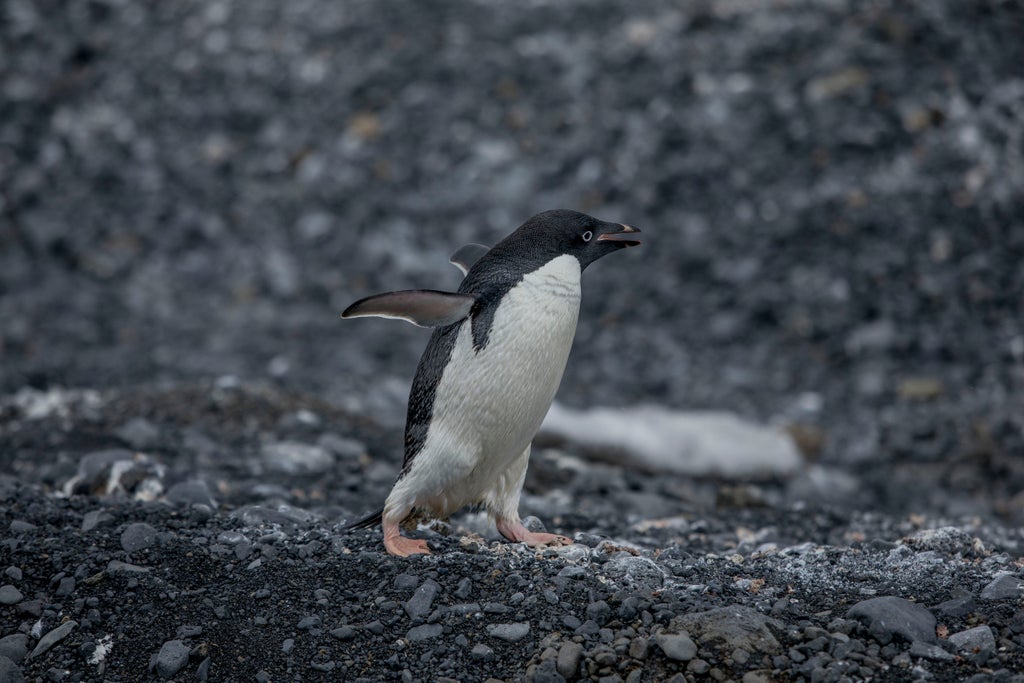

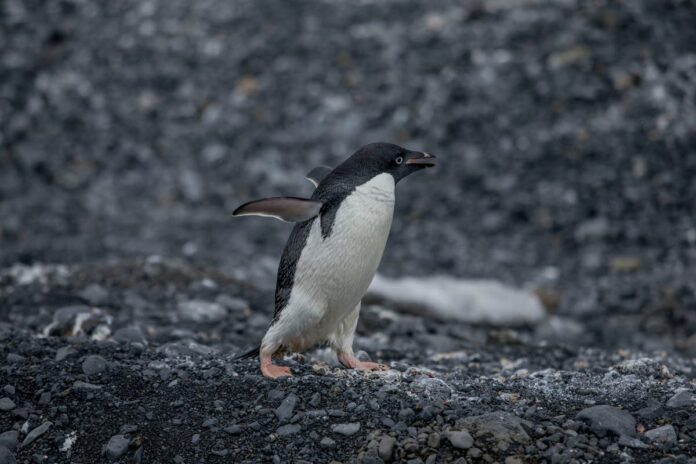
New penguin colonies have been discovered in the Antarctic as rising temperatures linked to the climate crisis cause birds to move further south.
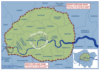
Researchers discovered a new colony of gentoo penguins at Andersson Island, on the eastern side of the Antarctic Peninsula, as well as the first-ever recorded findings of the species in an unexplored archipelago at the northern tip.
These are some of the southmost records for gentoo penguins in the region, where until recently it was too icy for the more temperate birds to successfully raise chicks.
Previously only one solitary gentoo nest had been found this far south. During a recent exploration, scientists discovered a colony of 75 gentoo chicks on Andersson Island.
Increased global heating, largely caused by the unabated burning of fossil fuels, is causing irreversible change to the polar regions including the rapid diminishing of ice sheets and glaciers.
The continent set a new record high temperature in February 2020, hitting 18.3C. The Antarctic Peninsula is among the fastest warming regions of Earth, heating up almost 3C over the last 50 years, World Meteorological Organization Secretary-General Prof. Petteri Taalas said at the time.
“This new temperature record is therefore consistent with the climate change we are observing,” he added.
Penguins can provide warnings on the overall health of the Antarctic ecosystem. Another recent expedition, for example, found that chinstrap penguin colonies at Elephant Island had collapsed, some by as much as 77 per cent in the last 50 years.
The gentoo penguin has a distinctive look with a white stripe across its head, a vivid reddish bill and a long tail which sweeps from side to side as it waddles.
They are the third-largest of the penguin species, after emperor and king penguins, and can grow up to 35 inches tall. They are also the fastest penguins when it comes to underwater swimming, reaching top speeds of 22mph.
Scientists are carrying out the first-ever counts of their colonies, filling vital data gaps about the status of the gentoos. The researchers were part of a Greenpeace expedition to the region onboard the Arctic Sunrise ship.
Dr Heather J. Lynch, professor of ecology & evolution at New York’s Stony Brook University, and an expedition lead, explained that the trip had involved surveying on foot, for the first time, parts of the peninsula where penguin colonies had been spotted from satellites.
“Mapping out these remote archipelagos will give us a better understanding of how the region’s penguins are responding to rapid climate change,” Dr Lynch said.
“As expected, we’re finding gentoo penguins nearly everywhere we look – more evidence that climate change is drastically changing the mix of species here on the Antarctic Peninsula.”
The findings were released on Thursday to mark World Penguin Awareness Day.
Louisa Casson, from Greenpeace’s Protect the Oceans campaign, described it as “the climate crisis happening right in front of our eyes”.
“In the Antarctic, one of the most remote places on Earth, we are seeing a ‘gentoofication’ process where this species of penguin is spreading into new habitat and breeding further south: a biological manifestation of sea ice loss,” she said.
She called for governments to agree to a new Global Ocean Treaty to deliver protection for at least 30 per cent of the world’s oceans by 2030.
“Penguins and people across the world can’t wait: we need politicians to get ocean protection done now,” she added.
[ad_2]
Source link